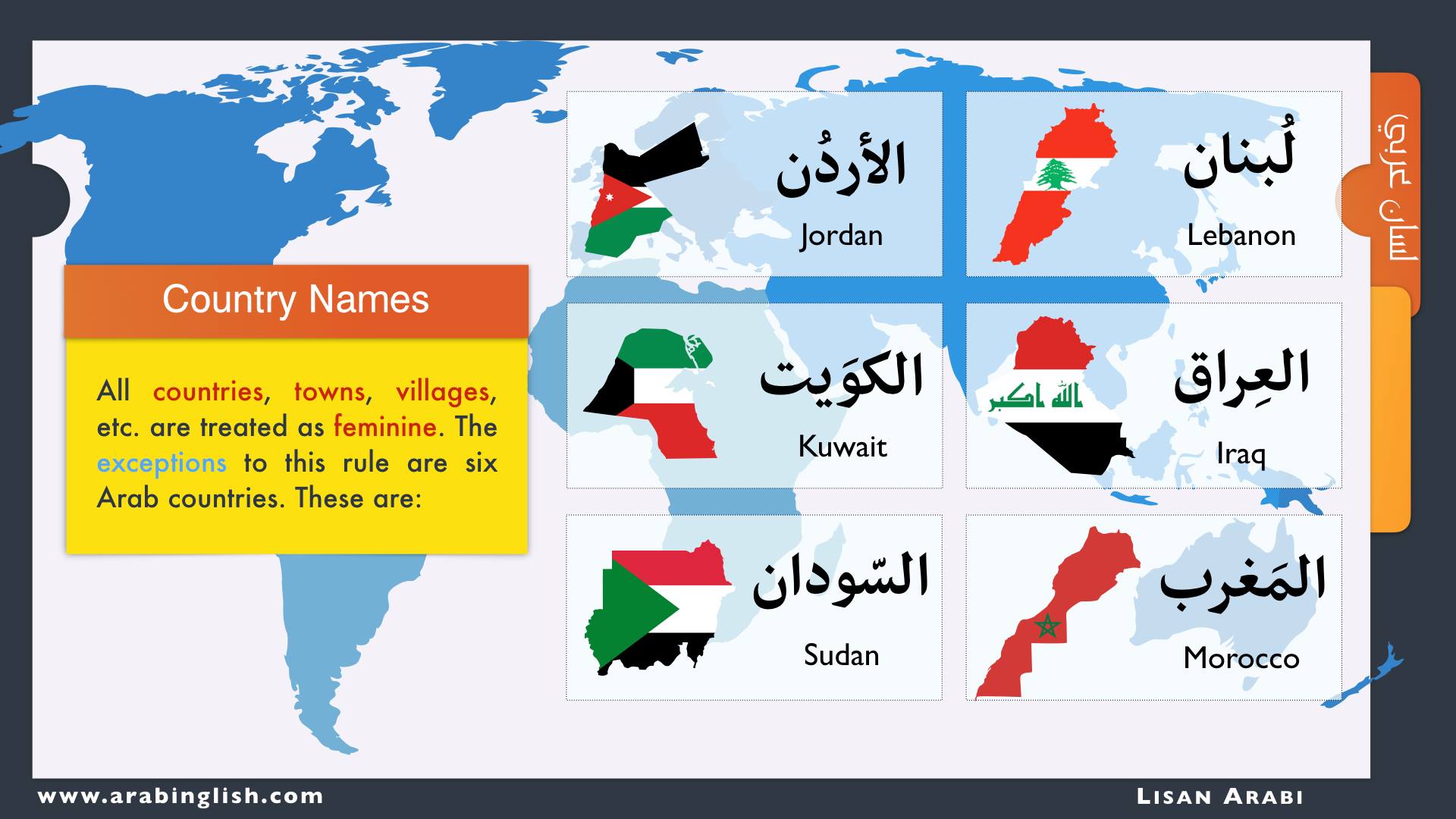
Gender
Nouns in Arabic can be either masculine or feminine.
MASCULINE nouns refer to male gender and have no sign of gender. they are noun from the meaning of the word, such as:
- Student [طالب ]
- Man [ رَجُل]
- book [ كتاب]
- king [ مَلك]
- pen [قلم]
FEMININE nouns refer to female gender and are of two types:
EXPLICIT: the word has feminine gender indicators as:
- taa marboutah [ ة ] :
- shortened alif [ ى ]:
- alif followed by hamza [اء]:

We usually change the masculine nouns by suffixing taa marbouta [ ة ] to the noun.

IMPLICIT: the word does not have any gender indicators such as:
- mother [ أم]
- daughter [بنت ]
- sun [شمس]
- eye [عين]
- ear [أذن]
There are some old masculine proper nouns end with tea marbouta such as:
معاوية ، حمزة ، عروة ، طلحة
Some nouns that end with (ى) as the last radical of the root verb are NOT feminine, such as:
- shelter [مأوى ]
- young man [فتى ]
- guidance [هُدى ]
Most names of body organs that are pairs such as eyes, ears, lungs, kidneys are feminine even if they don’t have feminine signs:
- kidney [كلية ]
- lung [رئة ]
- leg [رِجل ]
- hand [يد ]
- eye [عين ]
- ear [أذن ]
- testicle [ خصية]
Feminine words borrowed from other languages usually end with [ا]:
- France [فرنسا ]
- Germany [ ألمانيا]
- music [ موسيقا]
- mango [ مانجا]
- potatoes [بطاطا]
Some nouns that end with hamza after (ا) as the last radical of the verb are NOT feminine.
- judgement /jurisprudence [قضاء ]
- winter [ شتاء]
- building [ بناء]


Now try to do the quiz below to evaluate your understanding.
Gender
Look at the noun and choose whether it is feminine [مؤنث] or masculine [مذكر].

Podcast: Play in new window | Download